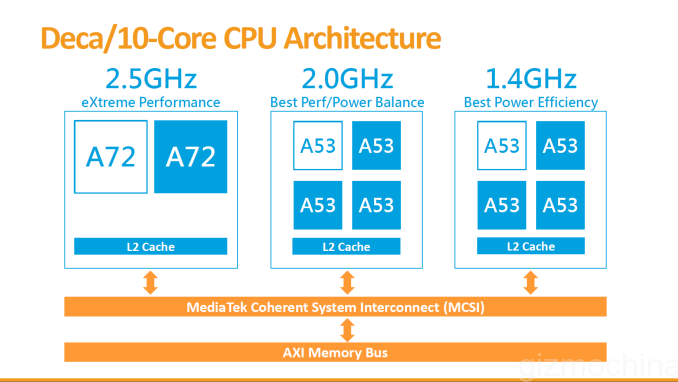
MediaTek has launched world’s first deca-core (ten processing cores) SoC with tri-cluster CPU architecture dubbed the MediaTek Helio X20. The first Helio SoC, Helio 10 was launched at Mobile World Congress 2015. The Helio X20 will take on Qualcomm Snapdragon 800 series, which has been incorporated in several flagship devices this year.
The MediaTek Helio X20 comes with three processor clusters which have designed to handle workloads with more efficiency. It comprises of two A72 cores clocked at 2.5GHz (for extreme loads), four A53 cores clocked at 2.0GHz (for medium loads) and four A53 cores clocked at 1.4GHz (for light loads). It will feature Mali T800 series GPU, however the exact model is not known yet.

The Helio X20 supports 32 mega pixel camera with 24fps and 25 mega pixel with 30 fps. On connectivity front, it supports LTE Cat., Wi-Fi 802.11ac, GPS and Glonass. It is also claimed to consume 30% less power as compared to erstwhile Helio X10 SoC. It will also come with support for dual main cameras and feature built-in 3D depth engine, multi-scale de-noise engines and embedded ARM Cortex-M4 processor
Highlights of MediaTek Helio X20
- Features tri-cluster CPU architecture with big.LITTLE arrangement
- Ten processing cores (Deca-core)
- Mali T800 series GPU
- Supports 32 mega pixel camera with 24fps, 25 mega pixel with 30 fps
- Embedded ARM Cortex-M4 processor
- Connectivity: LTE Cat., Wi-Fi 802.11ac, GPS and Glonass
“By leading with mobile CPU architecture and multimedia innovation, MediaTek continues to push the envelope of power efficiency and peak performance. We are excited to see device manufacturers raise the bar – in camera, display, audio and other consumer features. MediaTek has been adding innovative multimedia features to our platforms since the very beginning, enhancing the overall computing and multimedia experience as part of our strategy to put leading technology into the hands of everyone,” said Jeffrey Ju, Senior Vice President of MediaTek.
Also Read: Qualcomm Snapdragon 810 vs Predecessors: Which Is Better And Why?